(alt tax) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Image:small_buttonquail_alok.JPG|thumb|550px|right|Male, subspecies ''T. s. dussumier''<br />Photo © by {{user|aloktewari|Alok Tewari}}<br />Gurgaon Rural, Haryana, [[India]], July-2018]] | ||
| + | '''Alternative names: Small Buttonquail; Andalusian Hemipode; Kurrichane Buttonquail; Little Buttonquail''' (but this name also used for [[Little Buttonquail|Turnix velox]]) | ||
;[[:Category:Turnix|Turnix]] sylvaticus | ;[[:Category:Turnix|Turnix]] sylvaticus | ||
| + | |||
==Identification== | ==Identification== | ||
| − | + | 13–16 cm (5-6¼ in), female larger | |
| + | *face plain | ||
| + | *eyebrow pale | ||
| + | *upperparts streaked sandy brown | ||
| + | *underparts buff | ||
| + | *flank markings black | ||
| + | *wing grey with white wingbar | ||
| + | Sexes are similar | ||
| + | '''Immature birds''' have more spotted underparts | ||
| + | [[Image:small_buttonquail_alok_3.JPG|thumb|350px|right|Female, subspecies ''T. s. dussumier''<br />Photo © by {{user|aloktewari|Alok Tewari}}<br />Gurgaon Rural, Haryana, [[India]], July-2018]] | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | Southern [[Spain]] and [[Africa]] | + | Southern [[Spain]] and most of [[Africa]]. [[India]] and tropical [[Asia]] to [[Indonesia]]. |
| − | |||
==Taxonomy== | ==Taxonomy== | ||
| + | Reference [[#References|[4]]] notes that African and Asian subspecies often divided into "Kurrichane Buttonquail", ''T. sylvaticus'' (sspp. ''lepuranus'', ''sylvaticus'') and "Small Buttonquail", ''T. dussumier'' (sspp. ''bartelsorum'', ''celestinoi'', ''davidi'', ''dussumier'', ''nigrorum'', ''suluensis'', ''whiteheadi'') | ||
====Subspecies==== | ====Subspecies==== | ||
| − | + | Clements recognises the following subspecies [[#References|[1]]]: | |
| − | *''T. s. sylvaticus'' | + | *''T. s. sylvaticus'': "'''Kurrichane Buttonquail'''". Southern Iberian Peninsula, northern [[Morocco]], [[Algeria]] and [[Tunisia]] |
| − | *''T. s. lepuranus'' | + | *''T. s. lepuranus'': "'''Kurrichane Buttonquail'''". [[Africa]] south of the Sahara and extreme south Arabian Peninsula |
| − | *''T. s. dussumier'' | + | *''T. s. dussumier'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". Extreme eastern [[Iran]] to [[India]] and [[Burma]] |
| − | *''T. s. davidi'' | + | *''T. s. davidi'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". Peninsular [[Thailand]] to south [[China]], northern [[Indochina]] and [[Taiwan]] |
| − | *''T. s. whiteheadi'' | + | *''T. s. whiteheadi'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". Luzon Island (n [[Philippines]]) |
| − | *''T. s. nigrorum'' | + | *''T. s. nigrorum'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". Negros Island ([[Philippines]]) |
| − | *''T. s. celestinoi'' | + | *''T. s. celestinoi'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". South [[Philippines]] (Bohol and Mindanao) |
| − | *''T. s. suluensis'' | + | *''T. s. suluensis'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". Sulu Archipelago |
| − | *''T. s. bartelsorum'' | + | *''T. s. bartelsorum'': "'''Small Buttonquail'''". [[Java]] and [[Bali]] |
| − | + | [[Image:Small_Buttonquail_nothinghill.jpg|thumb|350px|right|Subspecies ''T. s. davidi''<br />Photo © by {{user|nothinghill|nothinghill}}<br />[[Thailand]], July-2012]] | |
==Habitat== | ==Habitat== | ||
| − | Grasslands or scrub jungle. Also cornfields and stretches of grassy plains. | + | Grasslands or scrub jungle. Also cornfields and stretches of grassy plains in [[Africa]]. |
==Behaviour== | ==Behaviour== | ||
| − | The diet | + | ====Diet==== |
| − | + | The diet consists of insects such as ants and seeds, particularly grass seeds. | |
| − | The female builds the nest which is a pad of grass placed in a natural hollow in the ground, amongst the stems of a tuft of grass. 4 speckled greyish eggs are incubated by the male who | + | ====Breeding==== |
| + | The female builds the nest which is a pad of grass placed in a natural hollow in the ground, amongst the stems of a tuft of grass. The 4 speckled greyish eggs are incubated by the male who cares for the [[Dictionary P-S#P|precocial]] young. | ||
| + | [[Image:small_buttonquail_alok_pair.png|thumb|350px|right|Breeding pair : larger female on right<br />Photo © by {{user|aloktewari|Alok Tewari}}<br />Gurgaon Rural, Haryana, [[India]], July-2018]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | #{{Ref- | + | #{{Ref-Clements6thAug17}}#Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive (retrieved July 2018) |
| + | #Wikipedia | ||
| + | #{{Ref-Eatonetal21}} | ||
{{Ref}} | {{Ref}} | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| − | {{GSearch|Turnix | + | {{GSearch|"Turnix sylvatic" {{!}} "Common Buttonquail" {{!}} "Small Buttonquail" {{!}} "Andalusian Hemipode" {{!}} "Kurrichane Buttonquail"}} |
| − | [[Category:Birds | + | {{GS-checked}}<br /><br /> |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Birds]] [[Category:Turnix]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:54, 27 August 2023
Alternative names: Small Buttonquail; Andalusian Hemipode; Kurrichane Buttonquail; Little Buttonquail (but this name also used for Turnix velox)
- Turnix sylvaticus
Identification
13–16 cm (5-6¼ in), female larger
- face plain
- eyebrow pale
- upperparts streaked sandy brown
- underparts buff
- flank markings black
- wing grey with white wingbar
Sexes are similar
Immature birds have more spotted underparts
Distribution
Southern Spain and most of Africa. India and tropical Asia to Indonesia.
Taxonomy
Reference [4] notes that African and Asian subspecies often divided into "Kurrichane Buttonquail", T. sylvaticus (sspp. lepuranus, sylvaticus) and "Small Buttonquail", T. dussumier (sspp. bartelsorum, celestinoi, davidi, dussumier, nigrorum, suluensis, whiteheadi)
Subspecies
Clements recognises the following subspecies [1]:
- T. s. sylvaticus: "Kurrichane Buttonquail". Southern Iberian Peninsula, northern Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia
- T. s. lepuranus: "Kurrichane Buttonquail". Africa south of the Sahara and extreme south Arabian Peninsula
- T. s. dussumier: "Small Buttonquail". Extreme eastern Iran to India and Burma
- T. s. davidi: "Small Buttonquail". Peninsular Thailand to south China, northern Indochina and Taiwan
- T. s. whiteheadi: "Small Buttonquail". Luzon Island (n Philippines)
- T. s. nigrorum: "Small Buttonquail". Negros Island (Philippines)
- T. s. celestinoi: "Small Buttonquail". South Philippines (Bohol and Mindanao)
- T. s. suluensis: "Small Buttonquail". Sulu Archipelago
- T. s. bartelsorum: "Small Buttonquail". Java and Bali
Habitat
Grasslands or scrub jungle. Also cornfields and stretches of grassy plains in Africa.
Behaviour
Diet
The diet consists of insects such as ants and seeds, particularly grass seeds.
Breeding
The female builds the nest which is a pad of grass placed in a natural hollow in the ground, amongst the stems of a tuft of grass. The 4 speckled greyish eggs are incubated by the male who cares for the precocial young.
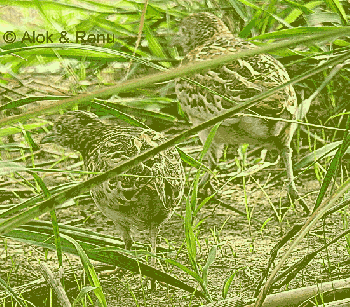
Photo © by Alok Tewari
Gurgaon Rural, Haryana, India, July-2018
References
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, D. Roberson, T. A. Fredericks, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2017. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2017, with updates to August 2017. Downloaded from http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/
- Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive (retrieved July 2018)
- Wikipedia
- Eaton, JA, B van Balen, NW Brickle, FE Rheindt 2021. Birds of the Indonesian Archipelago (Greater Sundas and Wallacea), Second Edition. Lynx Editions. ISBN978-84-16728-44-2
Recommended Citation
- BirdForum Opus contributors. (2024) Common Buttonquail. In: BirdForum, the forum for wild birds and birding. Retrieved 28 May 2024 from https://www.birdforum.net/opus/Common_Buttonquail
External Links
GSearch checked for 2020 platform.






