Alternative name: Amethyst Starling, Violet Starling
- Cinnyricinclus leucogaster
Identification
16cm. An unmistakable Starling:
Male
- Iridescent metallic purple head, throat, back and tail
- Deep purplish blue wings
- White breast and belly, occasionally lightly streaked
- Iris with yellow outer ring and dark inner ring
Female
- Brown head and back with streaked appearance (more uniform in arabicus)
- White belly, heavily streaked
Juveniles are similar to females.
Distribution
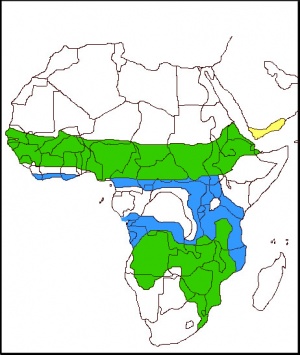
| Found in Africa south of the Sahara and in the southwest of the Arabian Peninsula. Widespread and common to abundant in its range. | |
| Legend • C. leucogaster; year-round |
Taxonomy
Subspecies
There are three recognized subspecies[1]:
- C. l. leucogaster:
- C. l. verreauxi:
- C. l. arabicus:
- Northern Ethiopia, Eritrea, eastern Sudan, north-western Somalia and Arabian Peninsula
Habitat
Mountain cliffs, savanna woodland (avoids thick evergreen forests), gardens, bushland near fruiting trees.
Behaviour
Diet
The diet includes fruit, especially figs, and some insects.
Forages mainly in trees and spends only little time on the ground.
Often associated with Greater Blue-eared Glossy-Starling and sometimes with Wattled Starling.
Breeding
They nest in tree holes lined with green leaves. The clutch consists of 2-4 pale blue oval eggs with reddish-brown spots. Incubated by the female for 2 weeks. Both adults care for the young for 3 weeks, feeding them mainly insects. Brood parasitism by Lesser Honeyguide recorded, possibly also host to Greater Honeyguide.
References
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, B.L. Sullivan, C. L. Wood, and D. Roberson. 2013. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: Version 6.8., with updates to August 2013. Downloaded from http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/
- Del Hoyo, J, A Elliott, and D Christie, eds. 2009. Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 14: Bush-shrikes to Old World Sparrows. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. ISBN 978-8496553507
- Avibase
- Paradise Earth
- BF Member observations
Recommended Citation
- BirdForum Opus contributors. (2025) Violet-backed Starling. In: BirdForum, the forum for wild birds and birding. Retrieved 25 April 2025 from https://www.birdforum.net/opus/Violet-backed_Starling
External Links
GSearch checked for 2020 platform.1