ShengTu Optics
Member
For bird watching enthusiasts, a pair of binoculars is a must. It not only helps us observe more details of birds, but also brings us aesthetic enjoyment and delights our souls! Binoculars should be of moderate size and weight, suitable for carrying at any time, comfortable for observation, with a wide field of view, very suitable for observing forest birds (forest birds are not far from the observer and move at a fast angular velocity), and very easy to operate! The requirements for bird watching binoculars are as follows:
1. Magnification: 7-10 times is more appropriate. Newbies often like to use high magnification, but the image jitter caused by high magnification will offset the detail recognition under high magnification. In addition, high magnification must be combined with a large-aperture objective lens to obtain a good observation effect, but a large aperture will directly increase the size and weight of the telescope, affecting portability. Therefore, the higher the magnification, the better. For ordinary people, 7-8 times is enough!

2. Aperture: The aperture refers to the diameter of the objective lens, which is generally between 20-50 mm. A small aperture means a small size, light weight, and good portability, but the image brightness is low and the observation comfort is poor. A large aperture means a large size, heavy weight, and poor portability, but the image brightness is high and the observation comfort is good. The common 20 and 25 mm apertures mainly highlight portability and are suitable for backup lenses. 30 and 32 mm apertures are a compromise between effect and portability, and 42 and 50 mm apertures mainly highlight the observation effect and are suitable for main lenses!

3. Exit pupil diameter and specifications: The exit pupil diameter is closely related to the image brightness and observation comfort. The calculation method of the exit pupil diameter is to use the objective lens diameter ÷ multiple. The 2.5 mm exit pupil diameter is suitable for bird watching in a brightly lit environment, such as 8X20/10X25. The advantage of these specifications is that they are small in size, light in weight and easy to carry, but the observation comfort is poor. The exit pupil diameter of about 4 mm can relax the requirements for light, such as 8X30/8X32/10X42, which can meet the bird watching requirements in most occasions. The exit pupil diameter of more than 5 mm is basically an all-weather type, especially suitable for observing birds at dusk and dawn, such as 8X42/10X50, with high brightness, clarity and comfort.

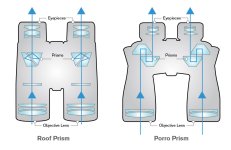
4. Prism: Prisms must be added to binoculars to obtain an erect image. Common prisms are divided into roof prisms and Porro prisms. Generally speaking, binoculars with roof prisms are more suitable for bird watching. Their appearance features two straight tubes in the lens barrel and a small distance between the centers of the objective lenses, which are suitable for observing close targets. It is also easy to make a nitrogen-filled waterproof structure, which is more suitable for harsh outdoor environments. Small size, light weight, and good portability! However, to obtain excellent observation results using roof prisms, high-precision prisms and complex coatings are required, and the high cost leads to high prices. Binoculars using Porro prisms have a curved appearance, a large distance between the centers of the objective lenses, and a long minimum observation distance. It is not easy to achieve a nitrogen-filled waterproof structure (high sealing can be achieved by using left and right independent focusing, but this focusing method is not suitable for bird watching), and they are large and heavy. However, the advantage is that the optical technology content is low, and good results can be obtained at a relatively low price. There is also a type of binoculars using anti-Porro prisms, which are relatively light, but have a small aperture and are not suitable for main telescopes.
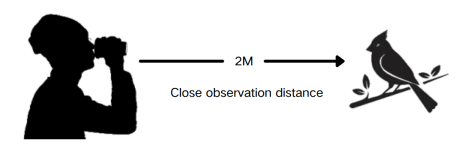
5,Minimum observation distance: Bird watching enthusiasts usually want a smaller minimum observation distance to observe birds hidden in bushes or grass. Binoculars using roof prisms can have a relatively small minimum observation distance, usually as close as 2 meters (for example, the Forester high-end 8X32 has a minimum observation distance of 1.2 meters), and binoculars using reverse Porro prisms can even have a minimum observation distance of less than 1 meter (for example, Pentax bug-eye binoculars can focus as close as 0.5 meters).
6. Focusing type: When observing forest birds, the distance between birds and people is sometimes far and sometimes close. Only by using central focusing can we adapt to the rapid changes in the distance of the observed object. Some central focusing Porro prism binoculars (such as Swarovski's HABICHT 8X30 binoculars) use O-rings to seal the movable eyepieces in order to achieve a waterproof structure, resulting in large focusing damping, and long-term operation will cause finger pain. As for left and right focusing Porro prism binoculars (such as military binoculars), the focusing speed is very slow and is not suitable for observing fast-moving birds.
(The left picture shows central focus, and the right picture shows independent focus)

7,Waterproof and shockproof: Bird watching activities are often conducted outdoors, and the observation environment is changeable. It is best to choose water-proof binoculars, so that the inside of the mirror can be kept sealed and dry, without fogging or mildew, and the service life of the telescope can be increased. For binoculars with rubberized surfaces, not only is the shockproof effect good, the optical axis is stable, but it is also more comfortable to hold.

8. Coating: For Porro prisms, it is enough to only coat them with anti-reflection coating. For roof prisms, reflective coating is necessary. To obtain good results, in addition to coating with anti-reflection coating, phase coating is also required. Therefore, when choosing a telescope, it is necessary to understand the various coating conditions of the telescope.
Anti-reflection coating: When light passes through the contact surface between glass and air, reflection will occur, which will not only reduce the brightness of the image, but also reduce the contrast of the image, making the image clarity lower. Therefore, it is necessary to coat the contact surface with anti-reflection coating to reduce reflection. Sometimes, in order to save costs, factories will omit the coating of the internal surface, or use a simple single-layer film. The use of multi-layer film will significantly reduce the reflection of light. The multi-layer film of domestic telescopes often presents a dark green reflection. A good telescope should be coated with multi-layer film on all necessary surfaces. This kind of telescope will be marked as FMC coating, but based on the commercial reputation of merchants in the current market, even if it is marked as FMC coating, it may not be true.

Phase film: Roof prism will split the light in the optical path into two beams. When they meet, the phases are opposite and interference occurs, resulting in blurred imaging. Phase film is used to compensate for the phase difference and eliminate interference (phase film is on the two surfaces of Figure 4 and 5). The use of this coating can improve the clarity of the image.


Reflective film: There is a surface in the roof prism that cannot fully reflect light (Figure 2), so a reflective film must be coated to reflect light. The conventional treatment method is aluminum coating, which has the advantage of not being easily oxidized, but has low reflectivity and the image is yellowish. It can also be silver-plated, which has the advantage of higher reflectivity than aluminum film, but has the risk of being oxidized, and the image is still yellowish. The best method at present is dielectric film coating, which has good stability, high reflectivity and small fluctuations with wavelength, so the image is bright and has no color cast.

9. Eye mask and pupil distance: For bird lovers with myopia/aging eyes/astigmatism, bird watching is different from viewing the scenery on the balcony. When viewing the scenery on the balcony, you can take off your glasses and slowly adjust the focus, while bird watching often requires wearing glasses to search for birds and then using binoculars to observe directly. Therefore, a soft eye mask that can be folded or rotated is required, otherwise the complete field of view cannot be observed. A very hard eye mask will make people very uncomfortable. In addition, the pupil distance should not be too short. The pupil distance below 15 mm will force the observer to put his eyes tightly behind the eyepiece, otherwise he will not be able to see the complete field of view.

Although binoculars have many advantages, if you want to observe more details or water birds, you need a high-power monocular bird-watching telescope. The requirements for a monocular bird-watching telescope are as follows:
1. Optical type: You must choose a short focal length refracting telescope with a waterproof structure. It is small in size and light in weight, with sharp images and good durability! (Reflective and reentrant telescopes are generally used in astronomical telescopes. They are complicated to operate, very large in size and weight, produce inverted images, may be observed from the side of the mirror body, and are not waterproof, so they are not suitable for bird watching or viewing)
2. Objective lens aperture: The aperture between 50-100 mm is more suitable. The aperture is closely related to the size, weight and magnification of the telescope. A too small aperture will result in a too low effective magnification of the telescope, which will not be able to play the role of fine observation. A too large aperture means a larger volume and weight. It is not an easy task for bird watchers to carry a big thing to climb mountains and wade through water. At present, the aperture of mainstream bird watching telescopes is about 80 mm. It will be lighter to choose an aperture of about 65 mm, and the matching tripod and gimbal can also be lighter.
3. Objective lens material: The objective lens of high-end monocular bird watching telescopes will be made of ED glass, and the objective lens of top-level monocular bird watching telescopes will be made of fluorite. ED glass and fluorite are expensive, and the processing yield is low, so the price is also expensive. Compared with ordinary optical glass, ED glass can effectively reduce chromatic aberration and improve the clarity of imaging, especially at high magnification. Fluorite is better than ED glass.

4. Eyepiece: Monocular bird-watching telescopes often come with zoom eyepieces (generally 20-60 times), which are easy to operate and use. Good zoom eyepieces have a larger field of view, less distortion, and a longer pupil distance. Some monocular bird-watching telescopes also provide fixed-focus eyepieces with different focal lengths as optional accessories, which can be used to obtain better observation results, but the operation is cumbersome when switching magnifications. In addition, unlike astronomical telescopes, the eyepieces of bird-watching telescopes of various brands are basically not universal.

5. Anti-reflection film: The use of anti-reflection film can also improve the brightness and contrast of the image, reduce flare and glare, and make the image brighter and clearer. Good anti-reflection films often present a dark green reflection. Some monocular bird-watching telescopes are based on cost considerations, and the surface of the internal lens is not coated (the surface coating of the external lens is easy to identify, so generally no corners are cut), or only a single layer of blue anti-reflection film is coated. It is recommended to give priority to monocular bird-watching telescopes with FMC coating!
6. Mirror body material: The top models will use aluminum-magnesium alloy to make the mirror body, which is firm and light. Common bodies are made of aluminum alloy, which is cheap and firm, and the density is only slightly higher than that of aluminum-magnesium alloy. The mirror body of low-end bird-watching mirrors is often made of plastic, which is very low in cost, but is prone to aging and deformation. A stable mirror body structure is a guarantee of optics and durability. It is recommended to choose a monocular bird-watching mirror with a metal mirror body!

7. Nitrogen filling and waterproofing: This is a very popular technology. Dry and clean nitrogen is injected into the sealed internal cavity of the telescope to prevent fogging and mildew inside the telescope and the invasion of dust and moisture. It can adapt to the changeable outdoor environment and greatly improve the service life of the telescope.
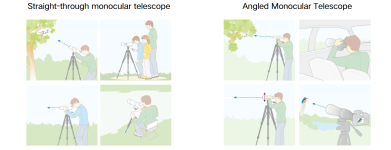
8. Oblique tube VS straight tube: It is generally recommended to choose an oblique tube as a bird-watching mirror, which has the most comfortable observation angle. If you choose a straight tube, you must raise the tripod to reach your eyes, which will reduce stability and the observation angle is not comfortable. However, the straight tube is more suitable for connecting a camera or mobile phone to shoot birds, because the line of sight and the direction of the telescope are consistent.
9. Tripod and pan head: Many beginners ignore the importance of tripod and pan head, and are often reluctant to spend money on them. It is very important to choose a light and reliable tripod. Lightness can reduce the burden when trekking in the wild, and reliability can improve the stability during observation. Carbon tripod is the best choice. Don't choose a ball head for the matching pan head. Choose a single-handle camera 3D pan head that controls the left and right and pitch. It is the simplest to operate. If conditions permit, it is recommended to choose a hydraulic pan head, which runs the smoothest.
1. Magnification: 7-10 times is more appropriate. Newbies often like to use high magnification, but the image jitter caused by high magnification will offset the detail recognition under high magnification. In addition, high magnification must be combined with a large-aperture objective lens to obtain a good observation effect, but a large aperture will directly increase the size and weight of the telescope, affecting portability. Therefore, the higher the magnification, the better. For ordinary people, 7-8 times is enough!

2. Aperture: The aperture refers to the diameter of the objective lens, which is generally between 20-50 mm. A small aperture means a small size, light weight, and good portability, but the image brightness is low and the observation comfort is poor. A large aperture means a large size, heavy weight, and poor portability, but the image brightness is high and the observation comfort is good. The common 20 and 25 mm apertures mainly highlight portability and are suitable for backup lenses. 30 and 32 mm apertures are a compromise between effect and portability, and 42 and 50 mm apertures mainly highlight the observation effect and are suitable for main lenses!

3. Exit pupil diameter and specifications: The exit pupil diameter is closely related to the image brightness and observation comfort. The calculation method of the exit pupil diameter is to use the objective lens diameter ÷ multiple. The 2.5 mm exit pupil diameter is suitable for bird watching in a brightly lit environment, such as 8X20/10X25. The advantage of these specifications is that they are small in size, light in weight and easy to carry, but the observation comfort is poor. The exit pupil diameter of about 4 mm can relax the requirements for light, such as 8X30/8X32/10X42, which can meet the bird watching requirements in most occasions. The exit pupil diameter of more than 5 mm is basically an all-weather type, especially suitable for observing birds at dusk and dawn, such as 8X42/10X50, with high brightness, clarity and comfort.

4. Prism: Prisms must be added to binoculars to obtain an erect image. Common prisms are divided into roof prisms and Porro prisms. Generally speaking, binoculars with roof prisms are more suitable for bird watching. Their appearance features two straight tubes in the lens barrel and a small distance between the centers of the objective lenses, which are suitable for observing close targets. It is also easy to make a nitrogen-filled waterproof structure, which is more suitable for harsh outdoor environments. Small size, light weight, and good portability! However, to obtain excellent observation results using roof prisms, high-precision prisms and complex coatings are required, and the high cost leads to high prices. Binoculars using Porro prisms have a curved appearance, a large distance between the centers of the objective lenses, and a long minimum observation distance. It is not easy to achieve a nitrogen-filled waterproof structure (high sealing can be achieved by using left and right independent focusing, but this focusing method is not suitable for bird watching), and they are large and heavy. However, the advantage is that the optical technology content is low, and good results can be obtained at a relatively low price. There is also a type of binoculars using anti-Porro prisms, which are relatively light, but have a small aperture and are not suitable for main telescopes.

5,Minimum observation distance: Bird watching enthusiasts usually want a smaller minimum observation distance to observe birds hidden in bushes or grass. Binoculars using roof prisms can have a relatively small minimum observation distance, usually as close as 2 meters (for example, the Forester high-end 8X32 has a minimum observation distance of 1.2 meters), and binoculars using reverse Porro prisms can even have a minimum observation distance of less than 1 meter (for example, Pentax bug-eye binoculars can focus as close as 0.5 meters).

6. Focusing type: When observing forest birds, the distance between birds and people is sometimes far and sometimes close. Only by using central focusing can we adapt to the rapid changes in the distance of the observed object. Some central focusing Porro prism binoculars (such as Swarovski's HABICHT 8X30 binoculars) use O-rings to seal the movable eyepieces in order to achieve a waterproof structure, resulting in large focusing damping, and long-term operation will cause finger pain. As for left and right focusing Porro prism binoculars (such as military binoculars), the focusing speed is very slow and is not suitable for observing fast-moving birds.
(The left picture shows central focus, and the right picture shows independent focus)

7,Waterproof and shockproof: Bird watching activities are often conducted outdoors, and the observation environment is changeable. It is best to choose water-proof binoculars, so that the inside of the mirror can be kept sealed and dry, without fogging or mildew, and the service life of the telescope can be increased. For binoculars with rubberized surfaces, not only is the shockproof effect good, the optical axis is stable, but it is also more comfortable to hold.

8. Coating: For Porro prisms, it is enough to only coat them with anti-reflection coating. For roof prisms, reflective coating is necessary. To obtain good results, in addition to coating with anti-reflection coating, phase coating is also required. Therefore, when choosing a telescope, it is necessary to understand the various coating conditions of the telescope.
Anti-reflection coating: When light passes through the contact surface between glass and air, reflection will occur, which will not only reduce the brightness of the image, but also reduce the contrast of the image, making the image clarity lower. Therefore, it is necessary to coat the contact surface with anti-reflection coating to reduce reflection. Sometimes, in order to save costs, factories will omit the coating of the internal surface, or use a simple single-layer film. The use of multi-layer film will significantly reduce the reflection of light. The multi-layer film of domestic telescopes often presents a dark green reflection. A good telescope should be coated with multi-layer film on all necessary surfaces. This kind of telescope will be marked as FMC coating, but based on the commercial reputation of merchants in the current market, even if it is marked as FMC coating, it may not be true.

Phase film: Roof prism will split the light in the optical path into two beams. When they meet, the phases are opposite and interference occurs, resulting in blurred imaging. Phase film is used to compensate for the phase difference and eliminate interference (phase film is on the two surfaces of Figure 4 and 5). The use of this coating can improve the clarity of the image.


Reflective film: There is a surface in the roof prism that cannot fully reflect light (Figure 2), so a reflective film must be coated to reflect light. The conventional treatment method is aluminum coating, which has the advantage of not being easily oxidized, but has low reflectivity and the image is yellowish. It can also be silver-plated, which has the advantage of higher reflectivity than aluminum film, but has the risk of being oxidized, and the image is still yellowish. The best method at present is dielectric film coating, which has good stability, high reflectivity and small fluctuations with wavelength, so the image is bright and has no color cast.

9. Eye mask and pupil distance: For bird lovers with myopia/aging eyes/astigmatism, bird watching is different from viewing the scenery on the balcony. When viewing the scenery on the balcony, you can take off your glasses and slowly adjust the focus, while bird watching often requires wearing glasses to search for birds and then using binoculars to observe directly. Therefore, a soft eye mask that can be folded or rotated is required, otherwise the complete field of view cannot be observed. A very hard eye mask will make people very uncomfortable. In addition, the pupil distance should not be too short. The pupil distance below 15 mm will force the observer to put his eyes tightly behind the eyepiece, otherwise he will not be able to see the complete field of view.

Although binoculars have many advantages, if you want to observe more details or water birds, you need a high-power monocular bird-watching telescope. The requirements for a monocular bird-watching telescope are as follows:
1. Optical type: You must choose a short focal length refracting telescope with a waterproof structure. It is small in size and light in weight, with sharp images and good durability! (Reflective and reentrant telescopes are generally used in astronomical telescopes. They are complicated to operate, very large in size and weight, produce inverted images, may be observed from the side of the mirror body, and are not waterproof, so they are not suitable for bird watching or viewing)

2. Objective lens aperture: The aperture between 50-100 mm is more suitable. The aperture is closely related to the size, weight and magnification of the telescope. A too small aperture will result in a too low effective magnification of the telescope, which will not be able to play the role of fine observation. A too large aperture means a larger volume and weight. It is not an easy task for bird watchers to carry a big thing to climb mountains and wade through water. At present, the aperture of mainstream bird watching telescopes is about 80 mm. It will be lighter to choose an aperture of about 65 mm, and the matching tripod and gimbal can also be lighter.

3. Objective lens material: The objective lens of high-end monocular bird watching telescopes will be made of ED glass, and the objective lens of top-level monocular bird watching telescopes will be made of fluorite. ED glass and fluorite are expensive, and the processing yield is low, so the price is also expensive. Compared with ordinary optical glass, ED glass can effectively reduce chromatic aberration and improve the clarity of imaging, especially at high magnification. Fluorite is better than ED glass.


4. Eyepiece: Monocular bird-watching telescopes often come with zoom eyepieces (generally 20-60 times), which are easy to operate and use. Good zoom eyepieces have a larger field of view, less distortion, and a longer pupil distance. Some monocular bird-watching telescopes also provide fixed-focus eyepieces with different focal lengths as optional accessories, which can be used to obtain better observation results, but the operation is cumbersome when switching magnifications. In addition, unlike astronomical telescopes, the eyepieces of bird-watching telescopes of various brands are basically not universal.

5. Anti-reflection film: The use of anti-reflection film can also improve the brightness and contrast of the image, reduce flare and glare, and make the image brighter and clearer. Good anti-reflection films often present a dark green reflection. Some monocular bird-watching telescopes are based on cost considerations, and the surface of the internal lens is not coated (the surface coating of the external lens is easy to identify, so generally no corners are cut), or only a single layer of blue anti-reflection film is coated. It is recommended to give priority to monocular bird-watching telescopes with FMC coating!

6. Mirror body material: The top models will use aluminum-magnesium alloy to make the mirror body, which is firm and light. Common bodies are made of aluminum alloy, which is cheap and firm, and the density is only slightly higher than that of aluminum-magnesium alloy. The mirror body of low-end bird-watching mirrors is often made of plastic, which is very low in cost, but is prone to aging and deformation. A stable mirror body structure is a guarantee of optics and durability. It is recommended to choose a monocular bird-watching mirror with a metal mirror body!

7. Nitrogen filling and waterproofing: This is a very popular technology. Dry and clean nitrogen is injected into the sealed internal cavity of the telescope to prevent fogging and mildew inside the telescope and the invasion of dust and moisture. It can adapt to the changeable outdoor environment and greatly improve the service life of the telescope.
8. Oblique tube VS straight tube: It is generally recommended to choose an oblique tube as a bird-watching mirror, which has the most comfortable observation angle. If you choose a straight tube, you must raise the tripod to reach your eyes, which will reduce stability and the observation angle is not comfortable. However, the straight tube is more suitable for connecting a camera or mobile phone to shoot birds, because the line of sight and the direction of the telescope are consistent.

9. Tripod and pan head: Many beginners ignore the importance of tripod and pan head, and are often reluctant to spend money on them. It is very important to choose a light and reliable tripod. Lightness can reduce the burden when trekking in the wild, and reliability can improve the stability during observation. Carbon tripod is the best choice. Don't choose a ball head for the matching pan head. Choose a single-handle camera 3D pan head that controls the left and right and pitch. It is the simplest to operate. If conditions permit, it is recommended to choose a hydraulic pan head, which runs the smoothest.






